Whisper Enhanced Transcription and Translation
This fork of OpenAI's Whisper provides an enhanced interface for audio transcription and translation. Using Streamlit, the app offers an interactive way to transcribe audio files to English and translate them into various languages.
Key Features
1. Automated Folder Creation for Each Transcription Run
- Each transcription is stored in a unique folder under a parent directory named
Results. - The folder is named based on the original audio file name and a timestamp, e.g.,
Results/[audio_file_name]_[timestamp], ensuring organized storage without overwriting previous transcriptions.
2. Temporary File Storage for Uploaded Audio Files
- Uploaded audio files are stored temporarily in a
TempUploadsfolder. - This separation helps manage temporary files separately from the main transcription results.
3. Interactive Web Interface with Streamlit (app.py)
- The main interface is
app.py, a web-based UI that enables users to upload audio files, select transcription models, and specify translation preferences. - Features:
- Upload Audio Files: Supports audio formats like MP3, WAV, M4A, and MP4.
- Choose Model Size: Users can select from Whisper’s model sizes (
tiny,base,small,medium,large) for transcription. - Specify Translation Language: After transcription to English, the text can be translated to languages like Turkish, Spanish, French, German, Chinese, and Japanese.
- Usage:
- First, install the necessary libraries (including Streamlit and googletrans):
pip install streamlit googletrans==4.0.0-rc1 - Run the app with:
streamlit run app.py - Open the app in your browser (usually at
http://localhost:8501).
- First, install the necessary libraries (including Streamlit and googletrans):
4. Translation Options with Google Translate Integration
- Once transcribed to English, the app can translate the text into various languages.
- Translation Workflow:
- Select a language from the
Translate Transcription Todropdown. - The app uses Google Translate to translate the English transcription to the selected language.
- Each translated text is stored in a
Translationssubfolder within the transcription folder, named[target_language]_translation.txt.
- Select a language from the
Example Workflow
- Upload an Audio File: Choose a file in MP3, WAV, M4A, or MP4 format.
- Select Transcription Options:
- Choose the model size for transcription.
- Select a language for translation, if desired (or leave as "None" for English-only transcription).
- View and Save Results:
- The app displays the English transcription and any selected translations.
- Transcriptions are saved in
Results/[audio_file_name]_[timestamp]/transcription.txt. - Translations are saved in
Results/[audio_file_name]_[timestamp]/Translations/[target_language]_translation.txt.
This enhanced setup offers a flexible, organized approach to audio transcription and translation, making Whisper accessible and powerful for multilingual projects.
These updates make app.py the primary and streamlined interface for managing transcriptions with Whisper. Temporary files and organized results folders ensure clear file management, while the web UI allows users to interact with Whisper effortlessly.
These enhancements make it easier to manage multiple transcription tasks, keep audio files and transcriptions organized, and provide an intuitive user interface for interacting with Whisper.
Whisper
[Blog] [Paper] [Model card] [Colab example]
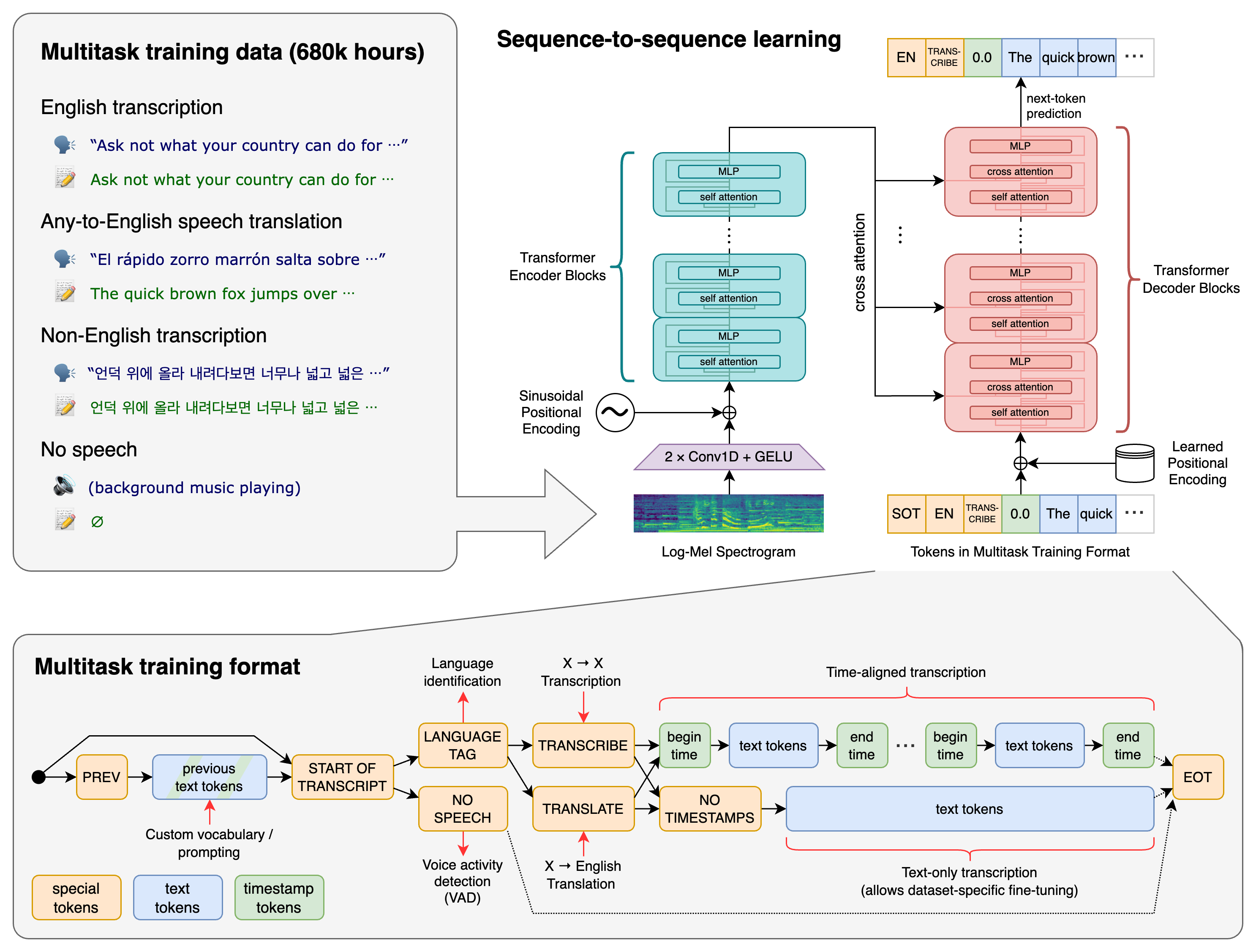
Whisper is a general-purpose speech recognition model. It is trained on a large dataset of diverse audio and is also a multitasking model that can perform multilingual speech recognition, speech translation, and language identification.
Approach
A Transformer sequence-to-sequence model is trained on various speech processing tasks, including multilingual speech recognition, speech translation, spoken language identification, and voice activity detection. These tasks are jointly represented as a sequence of tokens to be predicted by the decoder, allowing a single model to replace many stages of a traditional speech-processing pipeline. The multitask training format uses a set of special tokens that serve as task specifiers or classification targets.
Setup
We used Python 3.9.9 and PyTorch 1.10.1 to train and test our models, but the codebase is expected to be compatible with Python 3.8-3.11 and recent PyTorch versions. The codebase also depends on a few Python packages, most notably OpenAI's tiktoken for their fast tokenizer implementation. You can download and install (or update to) the latest release of Whisper with the following command:
pip install -U openai-whisper
Alternatively, the following command will pull and install the latest commit from this repository, along with its Python dependencies:
pip install git+https://github.com/openai/whisper.git
To update the package to the latest version of this repository, please run:
pip install --upgrade --no-deps --force-reinstall git+https://github.com/openai/whisper.git
It also requires the command-line tool ffmpeg to be installed on your system, which is available from most package managers:
# on Ubuntu or Debian
sudo apt update && sudo apt install ffmpeg
# on Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S ffmpeg
# on MacOS using Homebrew (https://brew.sh/)
brew install ffmpeg
# on Windows using Chocolatey (https://chocolatey.org/)
choco install ffmpeg
# on Windows using Scoop (https://scoop.sh/)
scoop install ffmpeg
You may need rust installed as well, in case tiktoken does not provide a pre-built wheel for your platform. If you see installation errors during the pip install command above, please follow the Getting started page to install Rust development environment. Additionally, you may need to configure the PATH environment variable, e.g. export PATH="$HOME/.cargo/bin:$PATH". If the installation fails with No module named 'setuptools_rust', you need to install setuptools_rust, e.g. by running:
pip install setuptools-rust
Available models and languages
There are six model sizes, four with English-only versions, offering speed and accuracy tradeoffs. Below are the names of the available models and their approximate memory requirements and inference speed relative to the large model. The relative speeds below are measured by transcribing English speech on a A100, and the real-world speed may vary significantly depending on many factors including the language, the speaking speed, and the available hardware.
| Size | Parameters | English-only model | Multilingual model | Required VRAM | Relative speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tiny | 39 M | tiny.en |
tiny |
~1 GB | ~10x |
| base | 74 M | base.en |
base |
~1 GB | ~7x |
| small | 244 M | small.en |
small |
~2 GB | ~4x |
| medium | 769 M | medium.en |
medium |
~5 GB | ~2x |
| large | 1550 M | N/A | large |
~10 GB | 1x |
| turbo | 809 M | N/A | turbo |
~6 GB | ~8x |
The .en models for English-only applications tend to perform better, especially for the tiny.en and base.en models. We observed that the difference becomes less significant for the small.en and medium.en models.
Additionally, the turbo model is an optimized version of large-v3 that offers faster transcription speed with a minimal degradation in accuracy.
Whisper's performance varies widely depending on the language. The figure below shows a performance breakdown of large-v3 and large-v2 models by language, using WERs (word error rates) or CER (character error rates, shown in Italic) evaluated on the Common Voice 15 and Fleurs datasets. Additional WER/CER metrics corresponding to the other models and datasets can be found in Appendix D.1, D.2, and D.4 of the paper, as well as the BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy) scores for translation in Appendix D.3.
Command-line usage
The following command will transcribe speech in audio files, using the turbo model:
whisper audio.flac audio.mp3 audio.wav --model turbo
The default setting (which selects the turbo model) works well for transcribing English. To transcribe an audio file containing non-English speech, you can specify the language using the --language option:
whisper japanese.wav --language Japanese
Adding --task translate will translate the speech into English:
whisper japanese.wav --language Japanese --task translate
Run the following to view all available options:
whisper --help
See tokenizer.py for the list of all available languages.
Python usage
Transcription can also be performed within Python:
import whisper
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
result = model.transcribe("audio.mp3")
print(result["text"])
Internally, the transcribe() method reads the entire file and processes the audio with a sliding 30-second window, performing autoregressive sequence-to-sequence predictions on each window.
Below is an example usage of whisper.detect_language() and whisper.decode() which provide lower-level access to the model.
import whisper
model = whisper.load_model("turbo")
# load audio and pad/trim it to fit 30 seconds
audio = whisper.load_audio("audio.mp3")
audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio)
# make log-Mel spectrogram and move to the same device as the model
mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio).to(model.device)
# detect the spoken language
_, probs = model.detect_language(mel)
print(f"Detected language: {max(probs, key=probs.get)}")
# decode the audio
options = whisper.DecodingOptions()
result = whisper.decode(model, mel, options)
# print the recognized text
print(result.text)
More examples
Please use the 🙌 Show and tell category in Discussions for sharing more example usages of Whisper and third-party extensions such as web demos, integrations with other tools, ports for different platforms, etc.
License
Whisper's code and model weights are released under the MIT License. See LICENSE for further details.